AI » OpenCL
2024-05-26 :: 7737 WordsOpenCL
概述
官网:
https://www.khronos.org/opencl/
OpenCL是一个硬件中立标准,原则上和计算机的体系结构无关。当然现实中,我们主要使用GPU进行运算加速。
和OpenGL、OpenVX的专用性不同,OpenCL主要定位于通用数学运算。OpenGL年代久远也就罢了。对于像OpenVX这样的新标准,有的时候其内部实现也有可能依赖于OpenCL。毕竟无论哪个领域的专用计算,最终都可以分解为基本的数学运算。
简单来说,OpenVX的封装粒度在Layer一级,而OpenCL最多只提供到矩阵运算一级的API。
https://chenxiaowei.gitbook.io/heterogeneous-computing-with-opencl2-0
OpenCL 2.0 异构计算 第三版 (中文)
https://cgmb-rocm-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Programming_Guides/Opencl-programming-guide.html
OpenCL Programming Guide
Reference Guide:
https://www.khronos.org/files/opencl-quick-reference-card.pdf
https://www.khronos.org/files/opencl20-quick-reference-card.pdf
https://www.khronos.org/files/opencl-1-2-quick-reference-card.pdf
OpenCL vs CUDA
| Term | CUDA | HIP | HC | C++AMP | OpenCL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Device | int deviceId |
int deviceId |
hc::accelerator |
concurrency::accelerator |
cl_device |
| Queue | cudaStream_t |
hipStream_t |
hc::accelerator_view |
concurrency::accelerator_view |
cl_command_queue |
| Event | cudaEvent_t |
hipEvent_t |
hc::completion_future |
concurrency::completion_future |
cl_event |
| Memory | void * |
void * |
void *; hc::array; hc::array_view |
concurrency::array;concurrency::array_view |
cl_mem |
| grid | grid | extent | extent | NDRange | |
| block | block | tile | tile | work-group | |
| thread | thread | thread | thread | work-item | |
| warp | warp | wavefront | N/A | sub-group | |
| Thread-index | threadIdx.x | hipThreadIdx_x | t_idx.local[0] | t_idx.local[0] | get_local_id(0) |
| Block-index | blockIdx.x | hipBlockIdx_x | t_idx.tile[0] | t_idx.tile[0] | get_group_id(0) |
| Block-dim | blockDim.x | hipBlockDim_x | t_ext.tile_dim[0] | t_idx.tile_dim0 | get_local_size(0) |
| Grid-dim | gridDim.x | hipGridDim_x | t_ext[0] | t_ext[0] | get_global_size(0) |
| Device Kernel | __global__ |
__global__ |
lambda inside hc::parallel_for_each or [[hc]] |
restrict(amp) |
__kernel |
| Device Function | __device__ |
__device__ |
[[hc]] (detected automatically in many case) |
restrict(amp) |
Implied in device compilation |
| Host Function | __host_ (default) |
__host_ (default) |
[[cpu]] (default) |
restrict(cpu) (default) |
Implied in host compilation. |
| Host + Device Function | __host__ __device__ |
__host__ __device__ |
[[hc]] [[cpu]] |
restrict(amp,cpu) |
No equivalent |
| Kernel Launch | <<< >>> |
hipLaunchKernel |
hc::parallel_for_each |
concurrency::parallel_for_each |
clEnqueueNDRangeKernel |
| Global Memory | __global__ |
__global__ |
Unnecessary / Implied | Unnecessary / Implied | __global |
| Group Memory | __shared__ |
__shared__ |
tile_static |
tile_static |
__local |
| Constant | __constant__ |
__constant__ |
Unnecessary / Implied | Unnecessary / Implied | __constant |
__syncthreads |
__syncthreads |
tile_static.barrier() |
t_idx.barrier() |
barrier(CLK_LOCAL_MEMFENCE) |
|
| Atomic Builtins | atomicAdd |
atomicAdd |
hc::atomic_fetch_add |
concurrency::atomic_fetch_add |
atomic_add |
| Precise Math | cos(f) |
cos(f) |
hc::precise_math::cos(f) |
concurrency::precise_math::cos(f) |
cos(f) |
| Fast Math | __cos(f) |
__cos(f) |
hc::fast_math::cos(f) |
concurrency::fast_math::cos(f) |
native_cos(f) |
| Vector | float4 |
float4 |
hc::short_vector::float4 |
concurrency::graphics::float_4 |
float4 |
HIP和HC都是AMD的ROCm平台的API。
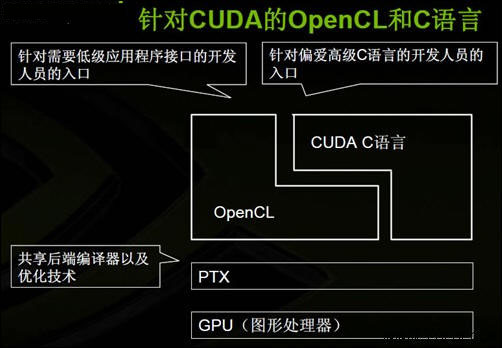
https://streamhpc.com/blog/2016-04-05/comparing-syntax-cuda-opencl-hip/
Comparing Syntax for CUDA, OpenCL and HiP
术语
kernel:内核就是在不同的异构设备上并行处理数据的单位。
平台模型:指定一个host处理器,用于任务的调度。以及一个或多个device处理器,用于执行OpenCL任务(OpenCL C Kernel)。这里将硬件抽象成了对应的设备(host或device)。
执行模型:定义了OpenCL在host上运行的环境应该如何配置,以及host如何指定设备执行某项工作。这里就包括host运行的环境,host-device交互的机制,以及配置内核时使用到的并发模型。并发模型定义了如何将算法分解成OpenCL工作项和工作组。
内核编程模型:定义了并发模型如何映射到实际物理硬件。
内存模型:定义了内存对象的类型,并且抽象了内存层次,这样内核就不用了解其使用内存的实际架构。
通常情况下,OpenCL实现的执行平台包括一个x86 CPU主处理器,和一个GPU设备作为加速器。主处理器会将内核放置在GPU上运行,并且发出指令让GPU按照某个特定的并行方式进行执行。内核使用到的内存数据都由编程者依据层级内存模型分配或开辟。运行时和驱动层会将抽象的内存区域映射到物理内存层面。最后,由GPU开辟硬件线程来对内核进行执行,并且将每个线程映射到对应的硬件单元上。
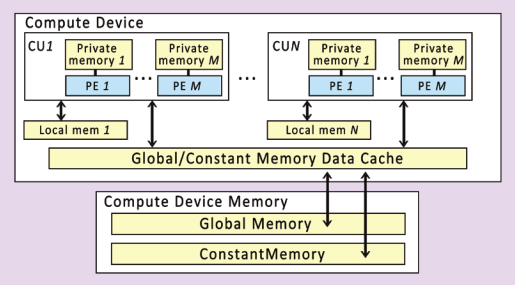
一个device可以被划分成一个或多个Compute Unit,这些CU在之后能被分成一个或多个Processing Elements。
执行内核的各个实例称为work-item。若干个同类的work-item组成一个work-group。
当要执行一个内核时,编程者需要指定每个维度上工作项的数量(NDRange)。一个NDRange可以是一维、二维、三维的,其不同维度上的工作项ID映射的是相应的输入或输出数据。
与工作项类似,工作组也需要从三个维度上指定,每个维度上的工作项有多少个。在同一个工作组中的工作项具有一些特殊的关系:一个工作组中的工作项可以进行同步,并且他们可以访问同一块共享内存。为了保证硬件工作效率,工作组的大小通常都是固定的。OpenCL也允许编程者不去分配工作组的尺寸,其会在实现中进行自动的划分。
内存对象与Context进行关联,而非某个设备。
与数组不同,图像数组数据不能直接访问。因为相邻的数据并不保证在内存上连续存储。使用图像的目的就是为了发挥硬件空间局部性的优势,并且可以利用设备硬件加速的能力。
管道内存对象就是一个数据元素(被称为packets)队列,其和其他队列一样,遵循FIFO(先进先出)的方式。为了支持“生产者-消费者”设计模式,一个内核与写入末尾点连接(生产者),同时另一个内核与读取末尾点连接(消费者)。
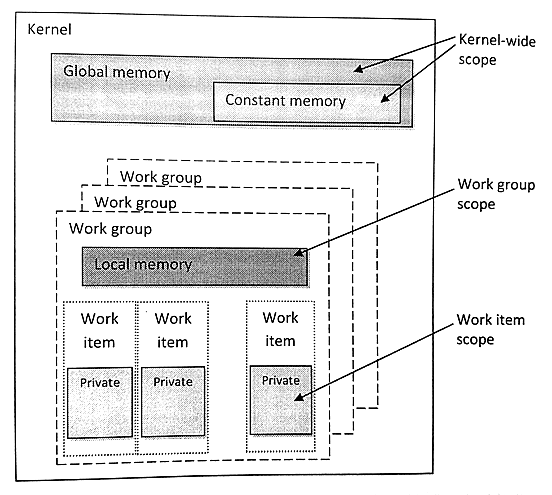
Kernel中,不同区域对应有不同的关键字,关键字用来指定变量使用哪种内存进行创建:__global、__constant、__local。通用地址空间支持指向私有、局部和全局地址指针的互相转换。
https://www.cnblogs.com/biglucky/p/3755189.html
kernel,work_item和workgroup
参考
https://github.com/microsoft/antares
Antares: an automatic engine for multi-platform kernel generation and optimization. Supporting CPU, CUDA, ROCm, DirectX12, GraphCore, SYCL for CPU/GPU, OpenCL for AMD/NVIDIA, Android CPU/GPU backends.
纹理坐标命名为s、t、r和q(与顶点坐标x、y、z和w类似)。
http://blog.csdn.net/leonwei/article/details/8880012
从零开始学习OpenCL开发(一)架构
https://programmerclick.com/article/47811146604/
Tutorial: Simple start with OpenCL and C++
SYCL
SYCL是Khronos提供的基于OpenCL的C++接口层。近来有向通用HPC发展的趋势,后端已不再限于OpenCL,开始包括OpenMP/CUDA等。
官网:
https://www.khronos.org/sycl
OpenCL-CLHPP
OpenCL-CLHPP的功能就要明确的多了,就是给OpenCL提供C++的API。
官网:
https://github.com/KhronosGroup/OpenCL-CLHPP
ComputeCpp
ComputeCpp是Codeplay公司提供的SYCL接口的实现。它除了支持OpenCL之外,还支持CUDA和C++AMP。
官网:
https://www.codeplay.com/products/computesuite/computecpp
其他实现
triSYCL:
https://github.com/triSYCL/triSYCL
DPC++:
https://github.com/intel/llvm/tree/sycl
hipSYCL:
https://github.com/illuhad/hipSYCL
前面几个是backend,以下是frontend:
libclc:
https://libclc.llvm.org/
PoCL
Portable Computing Language是另一个知名的OpenCL实现。
官网:
http://portablecl.org/
OpenCV+
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/pG5nq1fQ9XHp8WZN1AiLJQ
OpenCV基于Inception模型图像分类
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/EqeNS6s72_Qwg6mmDRl6wQ
OpenCV基于DLCO描述子匹配
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/JVuxMUmN2_DNfg1Ol5b8cw
OpenCV3新特性-图像无缝克隆函数演示
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/O3o8W1KSsZ0rz7aVukDWEg
使用OpenCV测量图像中物体之间的距离
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/HmOiQnkaqxcFPOODnOeUkw
使用OpenCV检测坑洼
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/BTmozO6Yr-Jsfm4-YXh2Mg
基于OpenCV的图像梯度与边缘检测
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QYnXiAMFC3k_wQIwiaeWQg
三行代码,OpenCV轻松生成19种色彩风格图像
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/4LQBY0rMJk0tU8lF3fgHfQ
基于OpenCV的图像阴影去除
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/kH6K6L6-BYnYE-g46WhNCg
在OpenCV中使用色彩校正
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/K4P8151BuM4DQPSK-KzPFQ
OpenCV图像旋转的原理与技巧
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/hGONFisdtwcF5CRSB9IF6g
图像处理基础:颜色空间及其OpenCV实现
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/0Z600IIGscgrREgLUqjLuA
手把手教你用Python做一个图像融合demo
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/vo1v5dYGLMqzCSUG9gPvag
使用OpenCV进行图像编辑–绘画和素描
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/EkxXV7Bizf4JxG15SQb79w
修改OpenCV一行代码,提升14%图像匹配效果(BEBLID(Boosted Efficient Binary Local Image Descriptor)是一个2020年才开发出来的算子)

您的打赏,是对我的鼓励
