toolchain » MLIR
2025-10-17 :: 6461 WordsMLIR
Multi-Level IR
代码:
llvm/mlir
教程:
llvm/mlir/docs/Tutorials/Toy
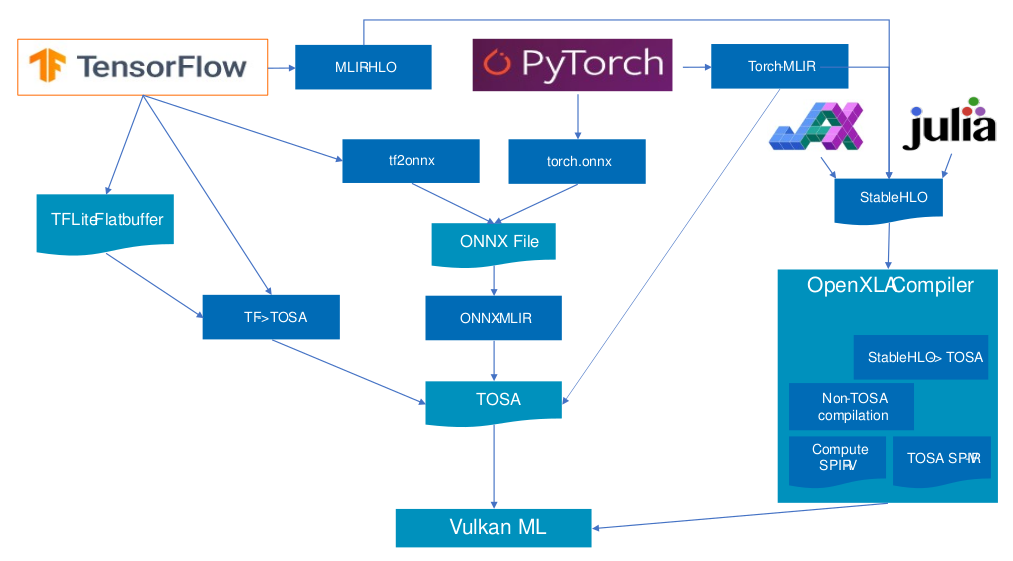
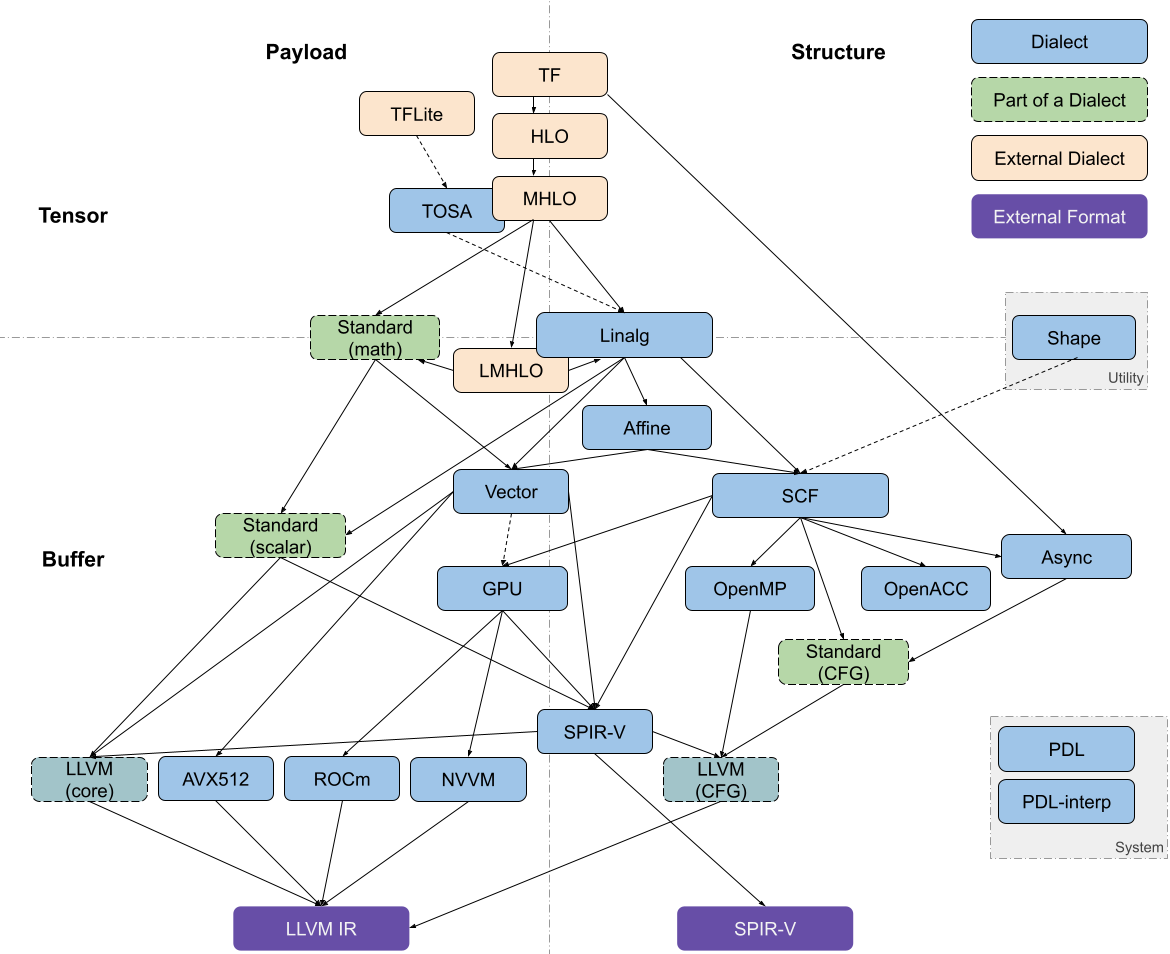
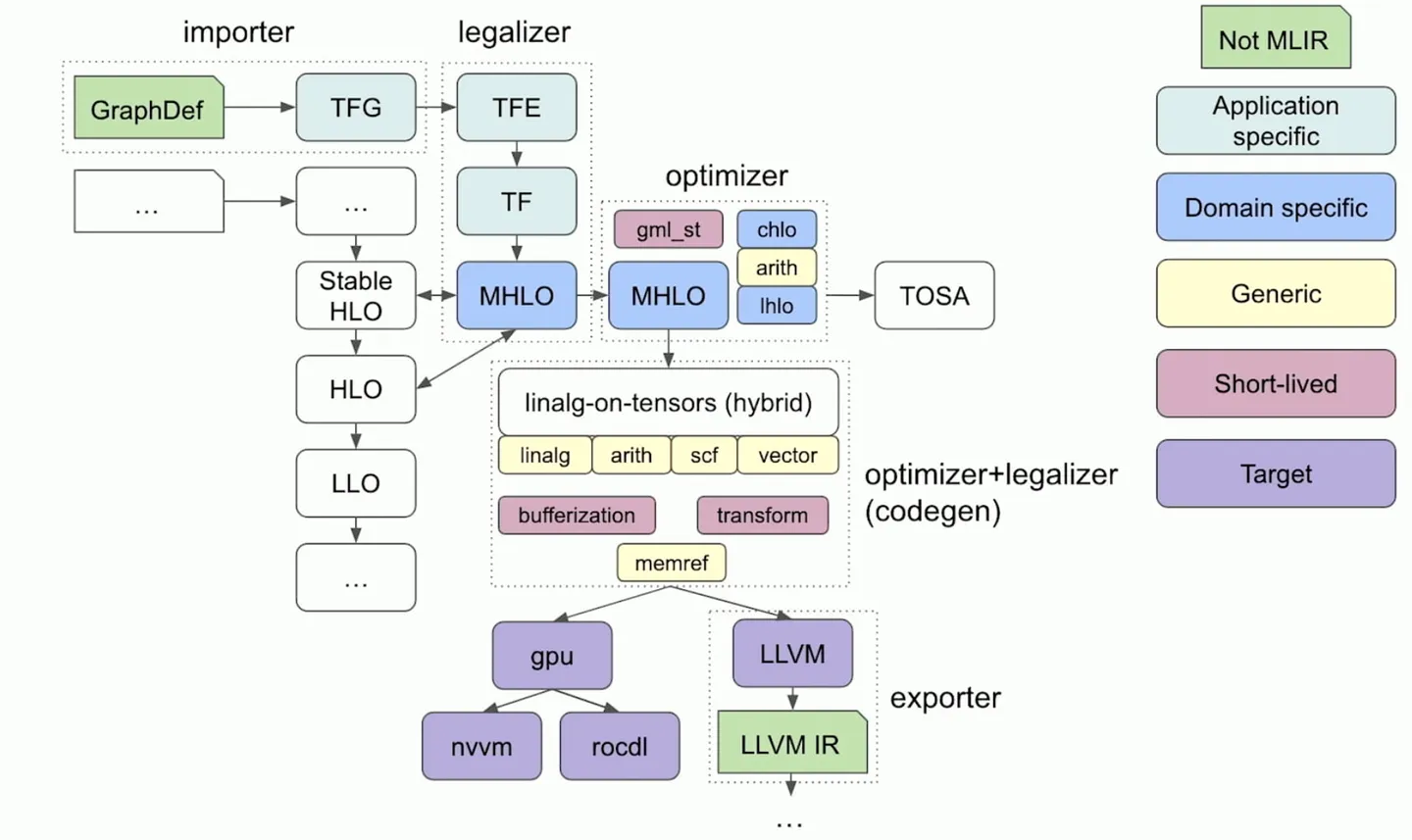
Affine Dialect:这种Dialect使用来自多面体编译的技术使依赖分析和循环转换高效可靠。
GPU Dialect:MLIR中的GPU Dialect模拟了类似于CUDA或OpenCL的通用GPU编程范式。它的目标是提供抽象来模拟GPU特定的操作和属性。它在很大程度上意味着与供应商无关。
Tensor Operator Set Architecture (TOSA) Dialect
Vector Dialect:对SIMD或者SIMT模型的抽象。
SCF(Structured Control Flow) Dialect:比控制流图CFG更高层的抽象,比如并行的for和while循环以及条件判断。
Async Dialect:通常用来表示异步操作模型。
Data Layout and Target Information (DLTI) Dialect
Control Flow Graph, CFG
Operation Definition Specification, ODS:“用一个.td文件把operation的完整签名、约束、接口、文档一次性声明清楚,再由TableGen自动生成所有C++代码”的框架。
mnemonic:dialect中的op name。
round-trip:把一段IR“先解析进来,再原样写回去”的完整循环。它主要用于验证parser/printer的正确性,并保留未注册的操作。
文档:
https://mlir.llvm.org/docs/Dialects/
参考:
https://discourse.llvm.org/t/codegen-dialect-overview/2723
Codegen Dialect Overview
Transform Dialect:dialect之间的调度变换都可以使用transform dialect中相关的语句来实现了,最终写成一个transform.sequence。相较于完整的Pipeline,transform.sequence实现的调度变换十分灵活。
官方文档:
https://mlir.llvm.org/docs/Tutorials/transform/
参考:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/624827690
transform dialect
ONNX MLIR:
http://onnx.ai/onnx-mlir
Torch-MLIR
https://github.com/llvm/torch-mlir
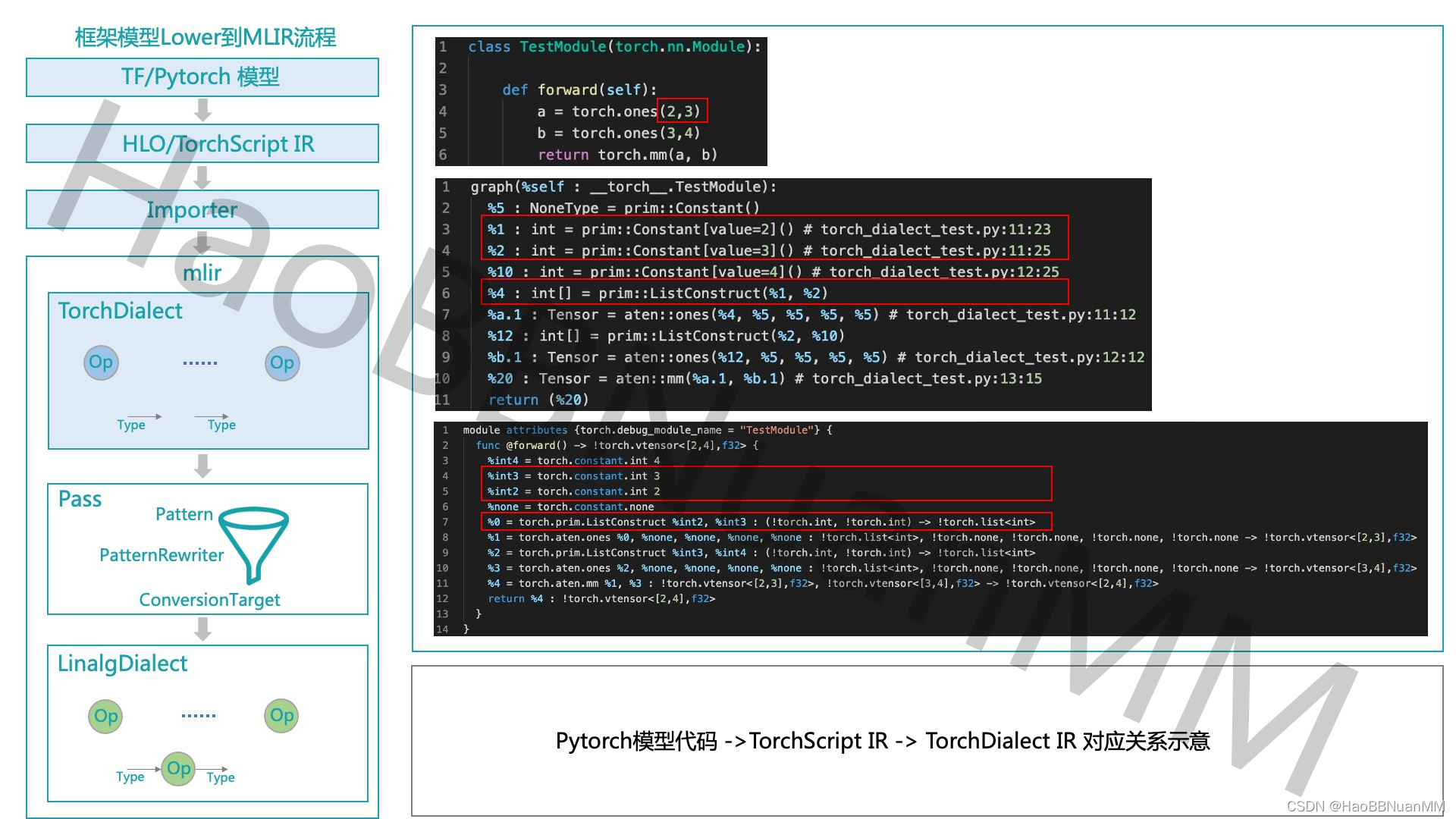
TorchScript–>TorchDialect–>Linalg-on-Tensors
https://blog.csdn.net/HaoBBNuanMM/article/details/124385542
Torch-MLIR技术详解
使用LLDB调试:
https://mlir.llvm.org/getting_started/Debugging/
插件:
https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project/blob/main/llvm/utils/lldbDataFormatters.py
https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project/blob/main/mlir/utils/lldb-scripts/mlirDataFormatters.py
./mlir-opt --pass-pipeline="builtin.module(func.func(tosa-to-linalg-named, tosa-to-linalg, tosa-to-arith{include-apply-rescale=1}, tosa-to-tensor),one-shot-bufferize,...)" a.mlir -o b.mlir
mlir-opt是一个命令行工具,用于组建Pass pipeline,将一个mlir文件变成另一个mlir文件。
TPP (Tensor Processing Primitives)
《Tensor Processing Primitives: A Programming Abstraction for Efficiency and Portability in Deep Learning & HPC Workloads》
TCP (Tensor Compute Primitives)
https://discourse.llvm.org/t/rfc-tile-dialect-and-or-dialect-reshuffle/71252
Tile Dialect and-or Dialect Reshuffle
MLIR是树形结构,每个节点是Operation,Op可以组成Block,Block组成Region,而Region又可以嵌套在Op内部。
Operation指单个运算,运算内可以嵌套Region。
Block指基本块,基本块包含一个或多个Operation。
Region指区域,类似于循环体或函数体,包含若干Block。Region类似于C语言的作用域,Region内可定义局部变量。
#map = affine_map<(m, n, k) -> (m, k)>
#map1 = affine_map<(m, n, k) -> (k, n)>
#map2 = affine_map<(m, n, k) -> (m, n)>
module {
func.func @main(%arg0: tensor<10x64xf32>, %arg1: tensor<64x16xf32>) -> tensor<10x16xf32> {
%0 = tensor.empty() : tensor<10x16xf32>
%1 = linalg.generic {indexing_maps = [#map, #map1, #map2], iterator_types = ["parallel", "parallel", "reduction"]} ins(%arg0, %arg1 : tensor<10x64xf32>, tensor<64x16xf32>) outs(%0 : tensor<10x16xf32>) {
^bb0(%in: f32, %in_0: f32, %out: f32):
%2 = arith.mulf %in, %in_0 : f32
%3 = arith.addf %out, %2 : f32
linalg.yield %3 : f32
} -> tensor<10x16xf32>
return %1 : tensor<10x16xf32>
}
}
上例是一个matmul算子的MLIR,linalg.generic表示了该指令属于linalg dialect。
Basic block指的是没有分支的代码序列,它使用^作为开头。
#map是一个属性别名,它使用#作为开头。
#foo<string<"">>:#还用于定义dialect的属性,<>内部是属性的body。
func.func定义函数,func.call调用函数,func.return函数返回。
async.func定义一个异步调用的函数,async.execute/async.call启动异步,async.await等待完成。
():函数参数、tuple。
[]:list。
{}:Region/Block、dict。
@:全局符号
$:局部符号
模式匹配:
Pattern Descriptor Language
https://mlir.llvm.org/docs/PDLL/
在PDLL之前,还有一个Tablegen DRR:
https://mlir.llvm.org/docs/DeclarativeRewrites/
Table-driven Declarative Rewrite Rule
./mlir-pdll -x=mlir rewrite.pdll
MLIR提供了mlir-tblgen和mlir-pdll工具,用于处理Tablegen和PDLL文件。
Pass:在MLIR内部对IR做转换,输入和输出都是MLIR。工具为mlir-opt。主函数mlir::MlirOptMain。
Translate:在MLIR边界做转换,输入或输出是非MLIR格式。工具为mlir-translate。
从文件的组织来看:
- Transforms文件夹做“内部优化/规范化”。所以一般是包含在某个Dialect名下的。
- Conversion文件夹做“Dialect到Dialect的逐步lowering”;
- Target文件夹做“最后一跳”,生成真正能让外部编译器/硬件直接消费的比特流或文本。Conversion和Target一般放在和Dialect同级的文件夹下。
当传入的参数过于复杂的时候,可以将参数写到文件中,然后使用以下技巧:
$(< file):把file的全部内容当成字符串返回,不启动子进程(比$(cat file)更快)。
declare_mlir_dialect_python_bindings:使用tblgen生成python bindings。
mlirOperationPrintWithFlags:Operation字符串化。
ConversionPatternRewriter:用于Dialect Conversion的PatternRewriter。
mlir-reduce的核心思路与llvm-reduce完全一致:
- 先由用户给出一个“判定脚本”,对输入
.mlir文件返回0表示“仍触发原 bug”(interesting),返回1表示“已不触发”。 - 在确保“仍触发”的前提下,mlir-reduce用各种办法反复裁减IR,直到剪到最小仍致命的IR片段。
SCF示例:
scf.for %iv = %lb to %ub step %step {
... // body
}
scf.if %b {
...
} else {
...
}
https://mlir.llvm.org/docs/Bindings/Python/
mlir-python-bindings
C API:
https://mlir.llvm.org/docs/CAPI/
model-explorer
model-explorer是google推出的可视化工具,支持对于MLIR的可视化。
官网:
https://github.com/google-ai-edge/model-explorer
安装&运行:
pip install ai-edge-model-explorer
model-explorer
pass
OpRewritePattern示例:
struct FoldAddIConstant : public OpRewritePattern<arith::AddIOp> {
FoldAddIConstant(MLIRContext *ctx)
: OpRewritePattern<arith::AddIOp>(ctx, /*benefit=*/1) {}
LogicalResult matchAndRewrite(arith::AddIOp op,
PatternRewriter &rewriter) const override {
...
auto newConst = rewriter.create<arith::ConstantIntOp>(
op.getLoc(), newVal, op.getType());
rewriter.replaceOp(op, newConst);
return success();
}
};
参考
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/fal6vz9gaZMbR41QMGE3AQ
MLIR发布:全新的中介码与编译器框架
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/361448250
MLIR Toy Tutorials
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/141256429
MLIR文章视频汇总
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/379063169
MLIR: 编译器基础架构重定义
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/508345356
AI编译器的概览、挑战和实践
https://blog.csdn.net/just_sort/article/details/123624966
基于MLIR的矩阵乘法高性能GPU代码生成:一些早期结果
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/442140282
MLIR: A Brief Survey
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/545672504
MLIR原理与应用技术杂谈
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/513872467
面向ASIC设备的编译器框架:TVM or MLIR?
https://www.zhihu.com/question/442964082
如何评价MLIR项目中Linalg Dialect的设计思想?
https://wzzju.github.io/mlir/jax/xla/2022/09/12/mlir-pass/
浅析MLIR在Pass优化中的应用
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/446836964
MLIR中Dialects分类及关联
https://www.lei.chat/zh/posts/mlir-codegen-dialects-for-machine-learning-compilers/
机器学习编译器代码生成相关MLIR Dialect
https://www.lei.chat/zh/posts/mlir-vector-dialect-and-patterns/
MLIR Vector Dialect以及Patterns
https://www.lei.chat/zh/posts/mlir-linalg-dialect-and-patterns/
MLIR Linalg Dialect以及Patterns
https://www.jeremykun.com/2023/08/10/mlir-running-and-testing-a-lowering/
MLIR — Running and Testing a Lowering
https://github.com/KEKE046/mlir-tutorial
Hands-On Practical MLIR Tutorial
https://www.cnblogs.com/BobHuang/p/18249482
从零开始教你写一个MLIR Pass

您的打赏,是对我的鼓励

